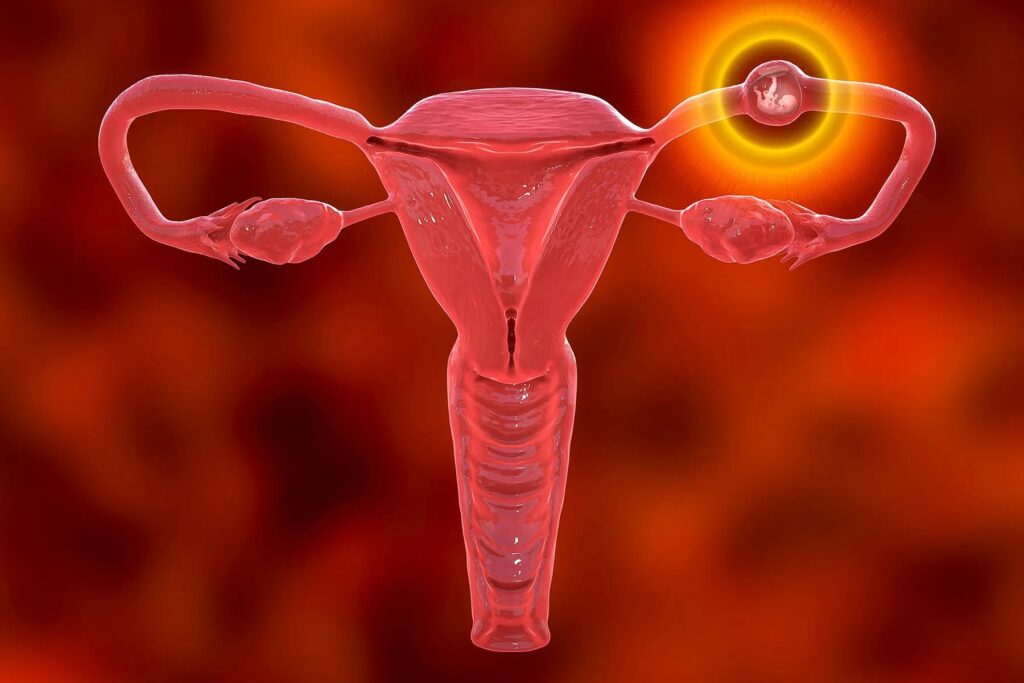
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. It cannot proceed normally and can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and managed promptly.
What Is Ectopic Pregnancy?
Normally, a fertilized egg travels to the uterus to implant and develop. In ectopic pregnancy, implantation occurs outside the uterus, most commonly in:
- Fallopian tubes (most common – called tubal pregnancy)
- Ovaries
- Abdominal cavity
- Cervix
Because the pregnancy cannot develop normally, it poses a risk of internal bleeding and serious complications if untreated.
Types of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Tubal pregnancy: Fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube (approx. 95% of cases).
- Ovarian pregnancy: Egg implants on the ovary.
- Cervical pregnancy: Implantation occurs in the cervix.
- Abdominal pregnancy: Implantation occurs in the abdominal cavity (rare).
Signs and Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Early detection is critical. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Missed period or pregnancy symptoms
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain (often one-sided)
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Dizziness or fainting (sign of internal bleeding)
- Shoulder pain (indicates internal bleeding)
- Nausea or vomiting
Symptoms usually appear between 4–12 weeks of pregnancy. If severe pain or heavy bleeding occurs, it is a medical emergency.
How Ectopic Pregnancy Is Managed
Management depends on the stage, location, and health of the woman. Options include:
- Medication (Methotrexate): Used in early, stable cases to stop cell growth.
- Surgical intervention: Required if the ectopic pregnancy is advanced or if there is internal bleeding. Types of surgery may include salpingectomy (removal of affected tube) or salpingostomy (removal of pregnancy while preserving tube).
- Close monitoring: Women with early, stable ectopic pregnancy may be closely monitored with ultrasounds and blood tests.
Interaction During Abortion and Importance of Ultrasound
Detecting ectopic pregnancy is critical before abortion or miscarriage management. Performing an abortion in the presence of an undiagnosed ectopic pregnancy can be dangerous.
Ultrasound is the primary diagnostic tool:
- Confirm intrauterine pregnancy
- Identify ectopic implantation
- Assess gestational age and health of reproductive organs
Clinicians always perform an ultrasound or a pregnancy assessment before abortion procedures to ensure safety and avoid complications from undiagnosed ectopic pregnancy.
Why Awareness Matters
Ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening if not detected early. Women experiencing unusual pain or bleeding in early pregnancy should seek medical attention immediately. Accurate diagnosis using ultrasound is essential before any abortion or miscarriage care.
Conclusion
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious reproductive health condition that requires prompt detection and management. Understanding the signs, types, and the role of ultrasound can help women make informed choices and access safe care. Pre-abortion assessment is crucial to prevent complications and protect women’s health.




