Can a girl get pregnant after having sex once?
Yes, it is possible for a girl to get pregnant after having sex once. Pregnancy can occur if sperm from the male partner fertilizes an egg released by the female partner during ovulation. Ovulation can occur at any time during a woman’s menstrual cycle, and even if the couple has sex only once, there is still a chance that it can result in pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to use contraception if the couple is not planning to conceive.
When are safe days?
It’s difficult to determine “safe days” for pregnancy prevention, as it depends on several factors such as the length of the menstrual cycle and timing of ovulation, which can vary from person to person. However, in general, the menstrual cycle starts on the first day of menstruation and ends on the day before the next menstrual period. The time between periods can vary but is usually around 28-32 days. Ovulation typically occurs around 14 days before the start of the next menstrual period.
To estimate the safe days for pregnancy prevention, one can use the fertility awareness method, which involves tracking basal body temperature, cervical mucus changes, and/or ovulation predictor kits. It is important to note that this method is not 100% effective and should be used in combination with other forms of contraception if pregnancy prevention is desired. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most effective contraception method for an individual’s specific needs.
Can an IUD the coil fail?
While an IUD (intrauterine device) or coil is a highly effective form of contraception, there is still a very small chance of it failing. The failure rate for IUDs is less than 1%, making it one of the most effective methods of contraception available. However, some factors that can increase the risk of IUD failure include incorrect insertion, expulsion, and perforation of the uterus during insertion. In rare cases, the IUD may also shift or become dislodged from its position, which can reduce its effectiveness.
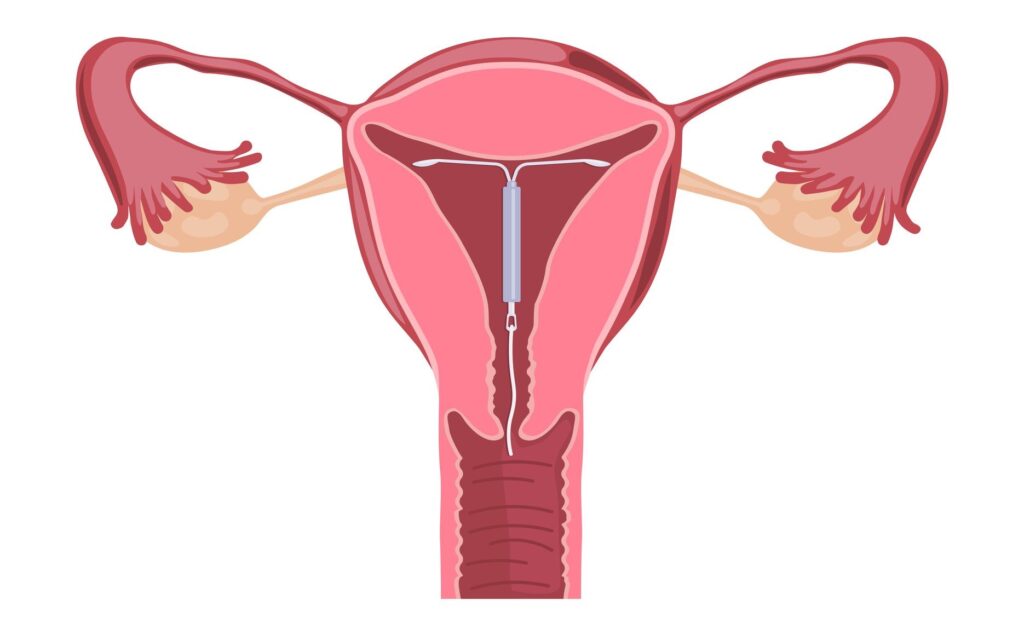
If a woman with an IUD experiences any symptoms such as severe pain, heavy bleeding, or loss of the device, she should seek medical attention immediately. Additionally, it’s important to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to ensure that the IUD is still in place and functioning correctly. Despite the small risk of failure, an IUD is still considered to be one of the most effective forms of contraception available.
Can you get pregnant from a burst condom?
If a condom breaks or bursts during sexual intercourse, there is a possibility of pregnancy. Condoms are designed to prevent pregnancy by creating a barrier that prevents sperm from reaching an egg. However, if the condom breaks, there is a chance that some of the sperm may enter the vagina and potentially fertilize an egg.
It’s important to take appropriate action immediately after a condom failure to reduce the risk of pregnancy. If a condom breaks during intercourse, the male partner should withdraw as soon as possible and replace the condom. If ejaculation has already occurred, the female partner may wish to consider using emergency contraception. Emergency contraception works by preventing or delaying ovulation, and should be taken as soon as possible after unprotected intercourse.
It’s also important to note that condoms can fail for a variety of reasons, such as incorrect use, expired or damaged condoms, or incompatible lubricants. To reduce the risk of condom failure, it’s important to use condoms correctly, check for damage before use, and use water-based lubricants. If condom failure occurs frequently, it may be worth exploring alternative methods of contraception with a healthcare provider.
Are pregnancies from cs-caesarian c section safe?
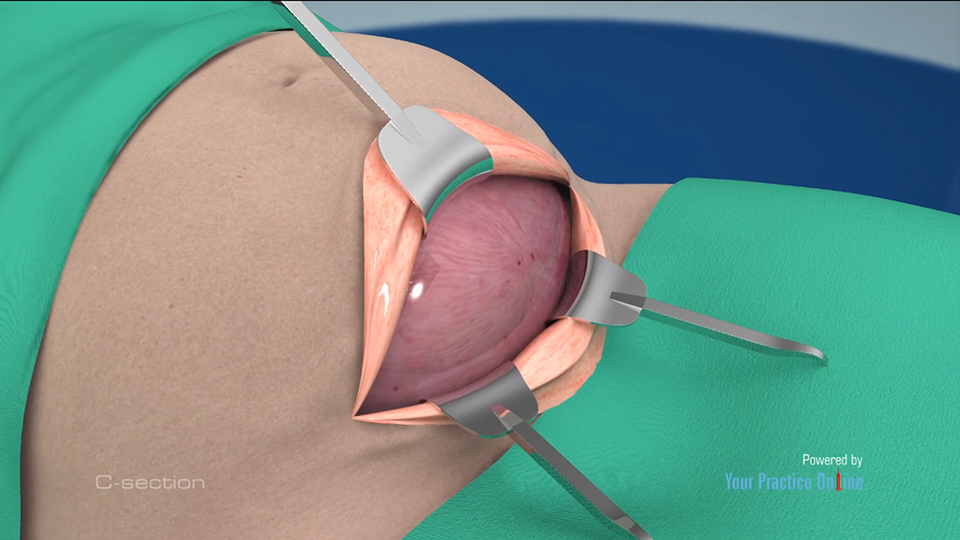
Yes, pregnancies following a previous caesarean section (C-section) can be safe, but there are some important considerations to keep in mind. Women who have had a previous C-section may be at a slightly increased risk of complications during subsequent pregnancies, such as uterine rupture or placenta previa, which is when the placenta covers part or all of the cervix. However, the vast majority of women who have had a previous C-section go on to have successful pregnancies and deliveries.
It is important for women who have had a C-section to discuss their options for delivery with their healthcare provider. In some cases, a planned repeat C-section may be recommended, while in other cases, a vaginal birth after C-section (VBAC) may be a safe option. Factors such as the reason for the previous C-section, the type of uterine incision, and the woman’s overall health and pregnancy status will all be taken into consideration when making this decision.
Overall, with appropriate monitoring and care, pregnancies following a C-section can be safe for both the mother and the baby. It’s important for women with a history of C-section to work closely with their healthcare provider to ensure the best possible outcomes for their pregnancies.
After birth how long can you get pregnant?
After giving birth, a woman can become pregnant again as soon as ovulation resumes, which can occur as early as 2-3 weeks after delivery. However, it is important to note that pregnancy soon after giving birth can carry additional risks, such as preterm labor, low birth weight, and other complications.
To reduce the risk of unintended pregnancy after giving birth, it is recommended to use a form of contraception. There are many safe and effective forms of contraception available, including barrier methods, hormonal methods, and long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) such as intrauterine devices (IUDs) and contraceptive implants.
It is important to discuss contraceptive options with a healthcare provider to determine the best method for an individual’s specific needs and preferences. Additionally, women who have recently given birth may need to wait for a certain period of time before certain types of contraception, such as hormonal methods, can be safely used.
Are abortion pills safe?
Abortion pills, when used correctly and under the guidance of a healthcare provider, are generally safe and effective for terminating early pregnancies. The two medications used in a medication abortion are mifepristone and misoprostol. Mifepristone is taken first, which blocks the hormone progesterone that is needed for a pregnancy to continue. Misoprostol is taken next, which causes the uterus to contract and expel the pregnancy.
Complications from medication abortion are rare, but can include heavy bleeding, infection, incomplete abortion, and allergic reactions. However, these complications can often be managed with appropriate medical care.
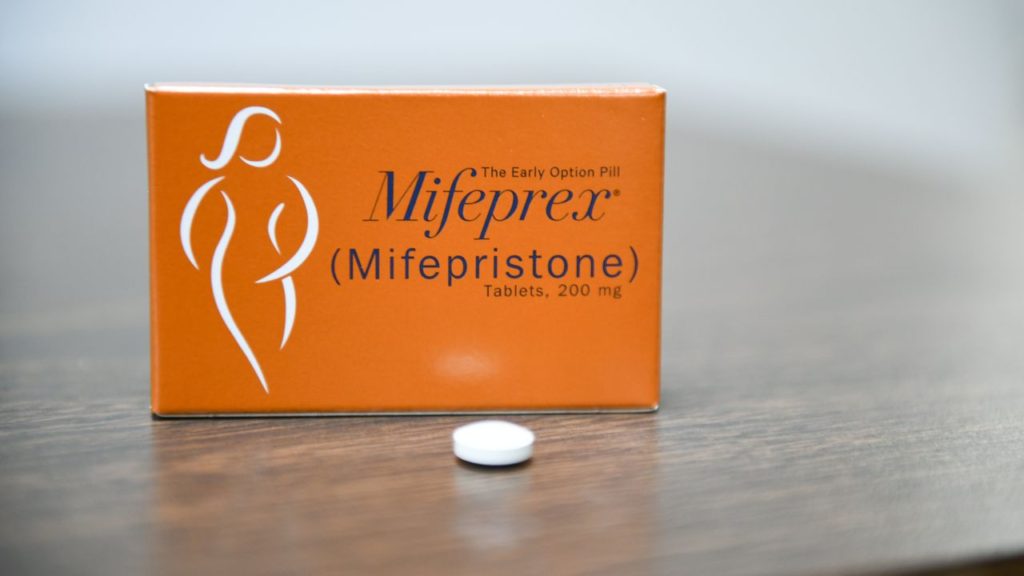
It’s important to note that medication abortion is only recommended for early pregnancies, typically up to 10 weeks of gestation. Women who are considering a medication abortion should consult with a healthcare provider to determine if it is a safe and appropriate option for them, and to receive instructions on how to take the medication and what to expect during and after the procedure.
It’s also important to access safe and legal abortion services, and to avoid unregulated or unsafe sources of medication for abortion. Access to safe and legal abortion services is a crucial aspect of reproductive healthcare, and can prevent serious complications and negative outcomes.
Can you get pregnant after having sex after periods
It is possible to get pregnant after having sex during or immediately after your period, although the chances are relatively low. A woman’s menstrual cycle is divided into two phases: the follicular phase (which includes menstruation) and the luteal phase. Ovulation, or the release of an egg from the ovary, typically occurs during the follicular phase, around 14 days before the start of the next period.
However, the exact timing of ovulation can vary from person to person and from cycle to cycle, and it is possible for ovulation to occur earlier or later than expected. Additionally, sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for several days, which means that it is possible to become pregnant from intercourse that occurs several days before ovulation.
Therefore, it is important to use contraception consistently and correctly if you want to prevent pregnancy. There are many safe and effective forms of contraception available, including barrier methods, hormonal methods, and long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) such as intrauterine devices (IUDs) and contraceptive implants. It is important to discuss contraceptive options with a healthcare provider to determine the best method for your specific needs and preferences.

What is pre cum?
Pre-cum, also known as pre-ejaculate or pre-cum fluid, is a clear fluid that is released from the penis during sexual arousal before ejaculation. Pre-cum is produced by the Cowper’s glands, which are located near the base of the penis. Its primary function is to lubricate the urethra and to neutralize any acidity in the urethra that may be present from residual urine.
Pre-cum may contain small amounts of sperm, which means that it is possible, though less likely than with ejaculation, to get pregnant from unprotected sex that involves contact with pre-cum. It is important to note that the risk of pregnancy from pre-cum is relatively low, but it is still possible. Therefore, it is recommended to use a form of contraception, such as condoms or other barrier methods, to prevent unwanted pregnancy and reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Can abortion affect your fertility?
In general, having a safe and legal abortion does not affect a woman’s fertility. The vast majority of women who have abortions are able to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term in the future, without any negative impact on their fertility.
However, there are some potential risks and complications associated with abortion that can affect fertility in rare cases. These may include infections or damage to the reproductive organs, particularly if the abortion is not performed under sterile conditions or if there are complications during the procedure.
It’s important to note that the risk of fertility-related complications from abortion is relatively low, and most women who have abortions do not experience any long-term effects on their fertility. It is important to access safe and legal abortion services, and to follow all post-abortion care instructions provided by a healthcare provider to minimize any potential risks and to promote overall reproductive health.
If you have concerns about the potential impact of abortion on your fertility, it is recommended to discuss these concerns with a healthcare provider who can provide personalized information and guidance based on your individual health history and circumstances.
Are abortions illegal in Kenya ?
Abortion is largely illegal in Kenya, except in certain circumstances where the life or health of the mother is at risk. The Kenyan constitution allows for abortion when there is a need for emergency treatment, or when the life or health of the mother is in danger and other forms of treatment have been exhausted. In addition, the Penal Code of Kenya provides for legal abortion in cases of rape or incest.
Despite these exceptions, access to safe and legal abortion services in Kenya is limited, and many women resort to unsafe abortion methods, which can lead to serious health complications and even death. In recent years, there have been efforts by women’s rights organizations and activists to advocate for expanded access to safe and legal abortion services in Kenya, but significant barriers remain.
It’s important for women to have access to safe and legal abortion services, as it is a crucial aspect of reproductive healthcare and can prevent serious complications and negative outcomes. If you are considering an abortion, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare provider who can provide accurate information about the options available and the risks and benefits of each.
Does Marie stopes offer abortion services?
Yes, Marie Stopes International is an international non-governmental organization that provides sexual and reproductive healthcare services, including safe and legal abortion services in countries where abortion is legal.
Marie Stopes International operates in over 37 countries worldwide and provides a range of sexual and reproductive health services, including contraception, STI testing and treatment, cervical cancer screening, and safe and legal abortion services.
However, it’s important to note that the specific services offered by Marie Stopes International may vary depending on the laws and regulations in each country. If you are seeking abortion services or any other reproductive healthcare services, it’s recommended to check the laws and regulations in your country and consult with a healthcare provider who can provide accurate information and guidance.
Are antibiotics needed after an abortion?
It depends on the type of abortion procedure and any potential risk of infection. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection after an abortion.
Surgical abortions, such as vacuum aspiration or dilation and curettage (D&C), carry a higher risk of infection compared to medication abortions. In these cases, antibiotics may be recommended to reduce the risk of infection.
Medication abortions, which involve taking medications to induce a miscarriage, typically do not require antibiotics unless there is a pre-existing infection or other risk factors for infection.
It’s important to follow the instructions of your healthcare provider and take any prescribed medications as directed. If you have any concerns or questions about antibiotics or other aspects of your abortion care, it’s best to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
What pills are used in abortion
There are two types of medication used in abortion: mifepristone and misoprostol.
Mifepristone, also known as RU-486, is a medication that blocks the hormone progesterone, which is needed for a pregnancy to continue. It is taken orally, usually in a clinic or doctor’s office, and works by causing the lining of the uterus to break down and the cervix to soften.
Misoprostol is another medication used in abortion. It is a prostaglandin that causes the uterus to contract and expel the contents of the pregnancy. It is taken orally or inserted vaginally, usually at home, 24-48 hours after taking mifepristone.
The combination of mifepristone and misoprostol is typically used for medication abortions in the first trimester of pregnancy, up to 10 weeks from the last menstrual period. In some cases, misoprostol may be used alone for abortions later in pregnancy or in cases where mifepristone is not available or contraindicated.
It’s important to note that the use of any medication for abortion should be supervised by a qualified healthcare provider, and that self-administration or use of unapproved medications can be dangerous and even life-threatening.




