Introduction
The issue of abortion is, perhaps, one of the most controversial topics on the agenda of the 21st century. Despite numerous debates and a consistent analysis of the issue, there has been no clear answer to whether it should be legalized or banned, and chances are that there never will be, due to the complicated ethical and religious dilemmas that need to be resolved to make a reasonable decision.
Unsafe abortion is one of the most neglected public health challenges in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, where an estimated one in four pregnancies are unintended—wanting to have a child later or wanting no more children. According to the World Health Organization, around 1.5 million abortions in MENA in 2010 were performed in unsanitary settings, by unskilled providers, or both. Complications from those abortions accounted for 11 percent of maternal deaths in the region.
Today, medical and scientific advances have made abortion a safe procedure when offered under medical supervision and with high standards of care. Yet each year, thousands of women in the developing world die and millions more are left with temporary or permanent disabilities because of unsafe abortion

Abortion for Kenyan women in the Middle East
Accessing abortion services in the Middle East countries is largely challenging apart for 3 countries Turkey, Tunisia and Israel that provide legal unconditional abortion services on request. However in 18 out of 47 muslin majority countries including Iraq, Egypt and Indonesia, abortion is only legally permitted if the life of the mother is threatened by the pregnancy.
Among socially conservative Muslim countries.7 countries permit abortion in the first 4 months of gestation for foetal deformities. The 4 countries in sub-Sahara Africa are Benin, Burkina Faso, Chad and Guinea.
The 3 in the Middle East are Kuwait, Qatar and Iran.
Most Middle East countries are very strict when it comes to matters abortion and with most of them being unsupportive/unfriendly on matters contraceptive. It proves to be quite a challenge.
Seeing that abortion rates are not going to decline in the observable future, there is a solid reason to consider the idea of making abortion legal in the Middle East, following the example of Turkey and Tunis. In other words, the basic principles, according to which pregnant women are treated in the Middle East, need to be reconsidered so that women could be granted a basic right to choose what is best for their health and further life.
It should be noted, though, that the process of providing Middle East women with their rights is going to be rather complicated, as it is likely to face a strong resistance from the citizens of the state, as well as the government thereof. Although the 20th and the 21st century can be viewed as the eras of breakthroughs as far as granting people with their irrefutable rights and freedoms are concerned, certain conservative viewpoints still hold the progress back, slackening its pace and setting the state back in its evolution. The above-mentioned problem is especially characteristic for the present-day feminist movements and the attempts at providing women with their rights and freedoms.
Abortion for women in Qatar
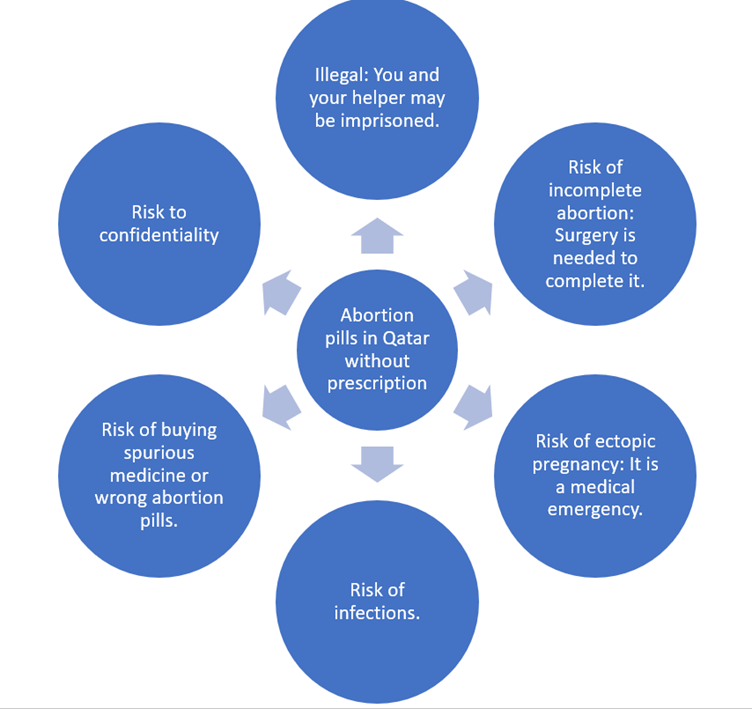
Abortion in Qatar is illegal in some circumstances. This post intends to educate you on the 6 most important things you should know before you buy abortion pills in Dubai, Sharjah, Ras al Khaimah, Abu Dhabi, Al Ain, Ajman, and Fujairah or anywhere in the UAE. Under Qatar’s penal code, a woman who induces her abortion or who consents to an abortion faces up to five years’ imprisonment. Individuals who perform an unauthorized abortion on a woman may face up to five years’ imprisonment if she consents, and up to ten years if it is performed without her consent.
This is why most Qatari women do pilgrimage abortions to countries such as India to have them conducted.
Abortion in the UAE
Abortion in the UAE is illegal, permissible only for married women in only two circumstances as per section 340 of the UAE penal code. These are:
- To save the woman’s life.
- In case the foetus has been detected with incurable disease or deformities. And abortion is permissible only for those deformities due to which the child to be born may not survive.
So, if your pregnancy is a result of failed contraceptives or rape or incest, you cannot get an abortion. Even if the ongoing pregnancy threatens your physical and/or mental health, abortion is not permissible.

